The growth hormone, also known as somatotropin, is produced and released by the pituitary gland situated at the brain’s base. This peptide hormone is essential for promoting the growth and development of the body’s cells, tissues, and organs.
Human Growth Hormone Benefits
Human growth hormone (HGH) is a peptide hormone from the pituitary gland essential for growth, body composition, cell repair, and metabolism. Recognizing what HGH will do for me helps highlight its importance in maintaining and improving bodily functions. Here are its primary benefits:
- Enhanced muscle strength. HGH promotes collagen synthesis in both skeletal muscles and tendons, leading to improved muscle strength and better exercise performance.
- Enhanced weight loss. Somatotropin increases lipolysis, breaking down lipids by hydrolyzing triglycerides into glycerol and free fatty acids. This process promotes fat loss and raises the metabolic rate.
- Stronger bones. If you don’t know what HGH does for the body, it regulates bone growth, particularly during puberty, by stimulating protein production that contributes to bone resorption and maintains bone mass and density.
- Reduced cardiovascular disease risk. Adequate somatotropin levels help maintain cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Better mood and cognitive function. HGH can improve psychological well-being, mood, and cognitive function, enhancing overall quality of life.
- Improved sleep patterns. It regulates sleep patterns, supports healthy circadian rhythms, and improves sleep quality, benefiting overall health.
HGH supplementation requires careful monitoring by healthcare providers due to potential risks like joint pain, muscle weakness, and abnormal growth patterns. Always consult a medical professional before starting HGH therapy.
Normal HGH Levels
Human growth hormone levels fluctuate throughout the day, influenced by age, gender, sleep, and physical activity. Doctors measure somatotropin levels through blood tests, using either a random measurement or a stimulation/suppression test for accuracy. Monitoring these levels helps diagnose and manage growth disorders, pituitary gland dysfunction, and other endocrine issues. Hormone norms:
- Children. HGH levels range from 0 to 20 ng/mL.
- Adults. HGH levels range from 0 to 10 ng/mL.
- Note. Random measurements vary widely due to the pulsatile nature of HGH secretion, making it less reliable for diagnostic purposes.
Factors Affecting HGH Levels

The level of growth hormone in the blood depends on:
- Age. HGH levels decline naturally with age. Peak levels occur during adolescence, a period of rapid growth and development. After the age of 20–30, HGH levels gradually decrease, aligning with the aging process and the reduced need for active growth and tissue repair.
- Physical activity. Regular exercise, particularly strength training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT), boosts human growth hormone levels. During exercise, muscles need more energy and recovery, which stimulates the production of growth hormone.
- Sleep. Deep, quality sleep, especially during the slow-wave phase, plays a crucial role in regulating pituitary-secreted growth hormone. The primary release of this hormone happens at night, so disrupted or insufficient sleep can significantly lower its levels.
- Stress. Chronic stress and elevated cortisol levels negatively impact growth hormone levels. Cortisol, known as the stress hormone, can block receptors responsible for HGH production, leading to decreased levels.
- Sex hormones. Sex hormones like testosterone and estrogen can influence HGH levels. During adolescence, their increase promotes higher somatotropin secretion, necessary for puberty and overall growth.
- Medications. Certain medications can affect HGH levels. For example, steroids and some types of hormone therapy can reduce production, while others, such as amino acid supplements or specific stimulants, can boost its levels.
- Genetic factors. Genetic predisposition also plays a significant role. Some individuals are genetically programmed to have higher or lower levels, which can explain individual differences in growth and metabolism.
Low Growth Hormone: What to Do?

Low levels of human growth hormone (HGH) can cause various health problems such as fatigue, reduced muscle mass, increased fat mass, and diminished overall well-being. Understanding what HGH is used for is crucial in addressing these issues effectively. If you suspect low HGH levels, take these steps to improve:
- Consult an endocrinologist for tests and evaluation of your HGH levels. Your doctor may prescribe hormone therapy or other treatments. He may also recommend somatropin HGH for sale (https://driadashop.eu/somatropin-hgh-liquid-100iu) , which you can purchase on Driada Medical Store.
- Improve sleep quality by aiming for 7–9 hours of deep, uninterrupted sleep nightly. Create a conducive sleep environment with a dark, quiet room and a comfortable bed.
- Integrate regular strength training and high-intensity interval training into your routine to enhance HGH levels through physical exercise.
- Manage stress with relaxation methods such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. Participate in calming hobbies or activities.
- Follow a balanced diet that includes ample protein, amino acids (particularly arginine), vitamins, and minerals. Reduce intake of sugar and high-glycemic carbohydrates.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake, as these habits can negatively affect hormone levels.
Following these steps and collaborating closely with your doctor can significantly enhance your growth hormone levels and overall health.
What Does HGH Do for Adults
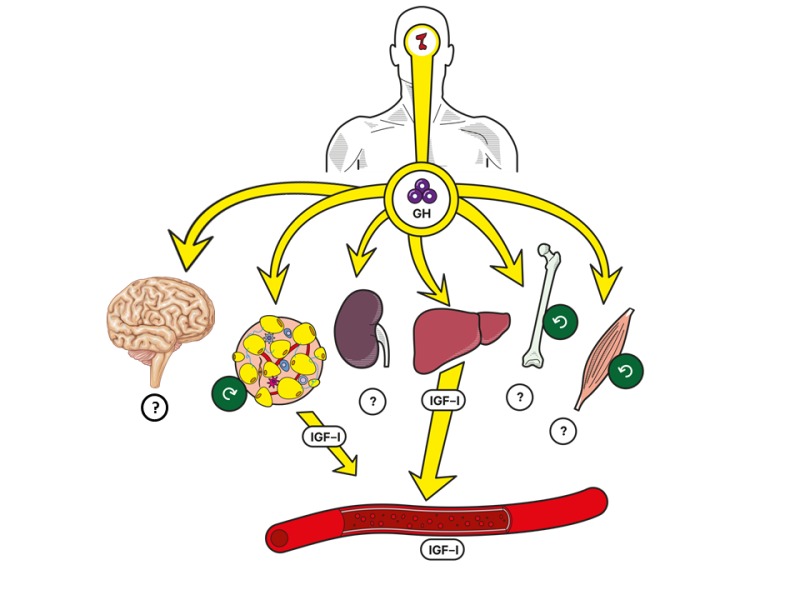
Human Growth Hormone (HGH) plays a crucial role in adult health and well-being. Here are the primary functions and benefits of somatotropin for adults:
- Metabolism regulation. Regulates metabolism by promoting fat breakdown and using carbohydrates and proteins for energy. Supports lean muscle mass maintenance and prevents fat accumulation.
- Muscle strength and mass. Stimulates muscle tissue growth and increases muscle strength. Enhances physical performance and aids in muscle recovery after exercise or injury.
- Bone density. Maintains bone density and strength. Stimulates the production of bone-forming cells, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
- Skin health. Maintains skin elasticity and thickness. Reduces wrinkles and improves skin tone and texture.
- Immune system support. Boosts the immune system by promoting immune cell production. Helps the body fight infections and recover from illnesses efficiently.
- Energy levels and mood. Contributes to higher energy levels and overall vitality. Improves mood and cognitive functions, enhancing mental clarity and reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- Cardiovascular health. Supports cardiovascular health by maintaining healthy cholesterol levels and reducing heart disease risk. Promotes blood vessel health and improves circulation.
- Healing and tissue repair. Accelerates tissue and wound healing. Aids in cell regeneration, promoting quicker recovery from injuries.
- Metabolic syndrome management. Improves insulin sensitivity and reduces abdominal fat. Lowers the risk of developing diabetes and cardiovascular conditions associated with metabolic syndrome.
HGH provides significant benefits for adults by supporting physical health, maintaining metabolic balance, enhancing physical performance, and promoting overall well-being.