In healthcare, the stakes couldn’t be higher when it comes to safety, effectiveness, and reliability.
Rigorous medical product testing ensures these standards are met, protecting patients and healthcare providers alike.
Testing serves as the backbone of regulatory compliance, safety assurance, and market success for medical products.
Regulatory Compliance

In the medical industry, ensuring regulatory compliance is more than a formality—it’s a safeguard against potential disasters.
Without proper compliance, products can pose serious safety risks, incur legal penalties, and damage reputations.
Regulatory compliance is a cornerstone of responsible healthcare procurement, setting a high bar for quality and reliability.
Key Standards and Certifications
Compliance with internationally recognized standards ensures that medical devices meet strict safety and performance benchmarks. Some key certifications and guidelines include:
- FDA (U.S.): Governs medical product approval, ensuring safety and efficacy before market release.
- CE Marking (Europe): Certifies products that conform to European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- ISO Standards (Global): Define specifications for quality management, product safety, and performance.
- IEC Guidelines: Focus on electrical and functional safety, critical for devices like diagnostic machines and surgical equipment.
Failure to meet these standards can result in severe consequences, including:
- Product recalls and financial losses.
- Legal liabilities and penalties.
- Increased risks to patient safety and institutional operations.
Impact on Decision-Making
Buyers play a pivotal role in upholding safety by prioritizing compliant products during procurement. Certifications assure of:
- Quality and Operational Efficiency: Ensuring reliable device performance.
- Enhanced Trust: Building confidence among patients, clinicians, and stakeholders.
- Reduced Liability Risks: Minimizing legal exposure for healthcare providers.
Identifying the Target Audience and Use Cases

Selecting the right medical products begins with a clear understanding of who will use them and under what circumstances.
Buyers must consider how a product’s design, functionality, and clinical effectiveness align with the needs of its intended users.
The approach is particularly important for life-saving tools like stop the bleed kits, which are designed for immediate and effective use in emergencies.
Demographics and Needs
The demographics and needs of the target audience are essential for ensuring that medical products meet clinical requirements.
Buyers should evaluate key factors about the end-user, such as:
- Age: Products for pediatric or geriatric use may require special design considerations.
- Medical Conditions: Devices must cater to the unique needs of conditions like diabetes, cardiovascular disease, or trauma care.
- Geographic Location: Remote or underserved areas may need robust and portable products.
Clinical Effectiveness Metrics
The effectiveness of medical products should be measured by their real-world impact on patient care.
Buyers should request data and case studies that showcase:
- Improved Diagnostics: Evidence of better accuracy in identifying medical conditions.
- Enhanced Treatment Outcomes: Success stories where the product significantly improved patient recovery.
- User Feedback: Input from healthcare professionals that helps refine and align the product with clinical needs.
Safety and Quality Assurance
Safety and quality assurance are critical aspects of medical product testing, ensuring that devices perform reliably and safely in real-world healthcare settings.
Rigorous protocols, comprehensive training, and regular maintenance are vital for minimizing risks and optimizing the lifespan of medical devices.
Essential Testing Protocols
To ensure the safety and effectiveness of medical devices, robust testing protocols must be implemented. These tests help identify potential flaws and confirm that devices meet the highest standards before reaching patients.
Key protocols include:
- Biocompatibility Testing: Ensures materials used in the device do not cause adverse reactions in patients.
- Durability Testing: Simulates long-term usage to assess the device’s performance over time.
- Usability Testing: Replicates real-world scenarios to validate the device’s functionality and user-friendliness.
- Stress and Failure Analysis: Evaluate how the device performs under extreme conditions, identifying potential failure points.
Technological and Functional Validations
Buyers should prioritize products that meet these advanced requirements, as they directly impact both patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
Interoperability and Modern Systems
Integration is a cornerstone of healthcare technology. Medical devices must communicate effectively with existing systems to maintain a seamless workflow and ensure accurate data exchange.
A lack of interoperability can lead to inefficiencies, data silos, and increased risk of errors.
- Ensure devices integrate with electronic health records (EHR) and hospital information systems.
- Verify compatibility with existing software and hardware infrastructure.
- Look for systems that enhance data sharing and reduce manual input errors.
Testing Non-Invasive and Advanced Technologies
Innovative technologies like robotic surgery systems and wearable diagnostics require advanced validation to ensure safety and reliability.
These devices represent the future of healthcare but carry higher stakes due to their complexity and critical use cases.
- Robotic systems should undergo simulation testing for precise, safe movements.
- Wearable devices must be tested for accuracy, durability, and user comfort in real-world scenarios.
- Advanced testing protocols should prioritize reducing patient risks while maintaining high performance.
Risk Management in Testing
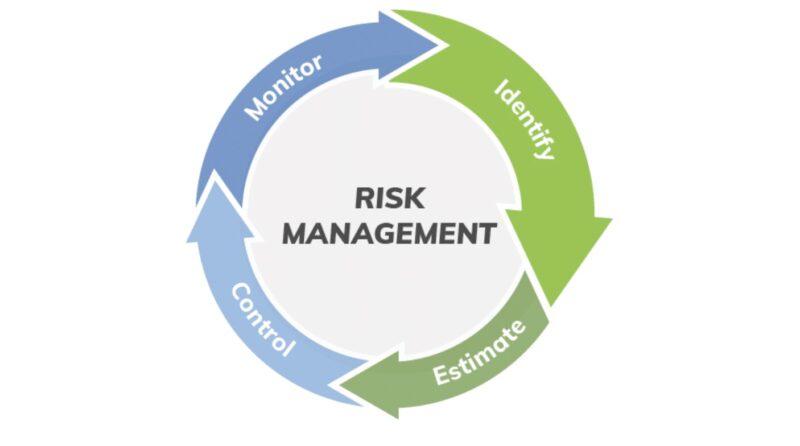
Effective risk management is a cornerstone of medical product testing.
Risks can emerge at any stage, from manufacturing to transport to regular use in clinical settings.
Buyers must prioritize products with thorough risk management protocols and demand ongoing monitoring even after the devices are in use.
The proactive approach can prevent costly failures and save lives.
Identifying Potential Hazards
Medical devices face numerous risks throughout their lifecycle. From production flaws to operational challenges, these hazards can compromise safety and efficiency. Buyers should carefully assess a manufacturer’s risk mitigation strategies to ensure robust safeguards are in place. Key steps include:
- Reviewing detailed risk assessment reports from manufacturers.
- Verifying testing protocols for identifying production and transport risks.
- Ensuring strategies are in place for mitigating risks during routine usage.
- Requesting data on past issues and how they were resolved.
Continuous Post-Market Surveillance
The need for vigilance doesn’t end once a product is released to the market. Continuous monitoring is essential to maintain performance and address unforeseen challenges. Manufacturers must provide buyers with tools and processes for effective post-market surveillance. Important aspects include:
- Mechanisms for real-time performance tracking and reporting.
- Systems to collect and analyze user data for identifying trends or issues.
- Regular compliance audits to ensure devices meet evolving safety standards.
- Processes for prompt corrective actions in response to detected problems.
Buyer Best Practices
Ensuring the safety, quality, and reliability of medical products starts with informed purchasing decisions.
Buyers must adopt proactive strategies to evaluate potential suppliers and their testing processes thoroughly.
Establishing clear expectations and asking the right questions can significantly reduce risks and enhance trust in the products being procured.
Testing Expectations
Buyers should require complete transparency from suppliers about their testing methodologies and results.
That includes full disclosure of compliance certifications, performance metrics, and usability studies.
A robust pre-purchase evaluation checklist ensures no critical aspect is overlooked.
- Insist on detailed testing documentation, including protocols and results.
- Ensure testing aligns with regulatory standards like FDA, CE, or ISO.
- Verify that products have undergone real-world usability and simulation testing.
Questions to Ask Suppliers
Asking the right questions during the procurement process helps identify reliable suppliers and ensures alignment with clinical needs. Consider the following:
- What tests have been conducted on the product, and what were the results?
- How is compliance with regulatory standards validated?
- What feedback from healthcare professionals or end-users influenced design iterations?
- Are post-market surveillance and reporting mechanisms in place?
The Bottom Line
Medical product testing is indispensable for ensuring safety, compliance, and operational success.
Buyers play a critical role by demanding rigorous testing and documentation from suppliers.
Proactive measures in procurement can safeguard lives, enhance trust, and foster innovation in healthcare.
Demand better testing, because lives depend on it.

