Gingival hyperplasia refers to an abnormal overgrowth of gum tissue around the teeth.
Recognizing and addressing this condition is critical, as it can affect oral health and overall well-being.
Early detection allows for timely management, ensuring healthier gums and a better quality of life.
Causes of Gum Overgrowth
Gingival hyperplasia is caused by a combination of factors, ranging from poor oral habits to underlying medical conditions. Recognizing these causes is essential for managing and preventing the condition.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Plaque and tartar buildup are among the leading causes of gum overgrowth. When oral hygiene is neglected, bacteria accumulate along the gumline, leading to inflammation.
This irritation can result in gum swelling and excessive tissue growth. Adopting consistent brushing and flossing routines helps minimize these risks.

Medications
- Anticonvulsants: Commonly prescribed for epilepsy, drugs like phenytoin may lead to excessive gum growth.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: Used for heart conditions and high blood pressure, these medications can affect gum tissue.
- Immunosuppressants: Drugs such as cyclosporine, often prescribed after organ transplants, are another contributing factor.
It is crucial to consult with healthcare providers when these medications cause gum-related issues.
Hormonal Changes

Hormonal fluctuations during life stages such as pregnancy, puberty, or menopause can lead to increased gum sensitivity and growth. Pregnancy gingivitis, for instance, is a condition where hormonal changes heighten gum inflammation.
Adolescents undergoing puberty may also notice changes in gum size due to heightened hormone levels. Maintaining excellent oral hygiene during these periods can help reduce inflammation.
Genetic Predisposition
Hereditary gingival fibromatosis is a rare genetic disorder causing excessive gum tissue growth. This condition typically manifests during childhood or adolescence.
Genetic factors can predispose individuals to gum overgrowth, even with good oral care practices. Dental professionals may suggest specialized treatment options for such hereditary cases.
Systemic Conditions
- Leukemia: This blood-related cancer can lead to gum swelling and other oral health issues.
- Diabetes: Poorly controlled diabetes can exacerbate gum inflammation, leading to overgrowth.
Monitoring systemic health and seeking dental care when abnormalities arise are vital in addressing these concerns.
Symptoms and Diagnosis

Gingival hyperplasia presents with several noticeable symptoms that can impact daily life and overall oral health.
These symptoms often begin subtly but can progress over time, becoming more pronounced and uncomfortable if left unaddressed.
- Swollen and tender gums: The gums may feel sensitive to the touch and appear visibly enlarged.
- Red or inflamed appearance: Healthy pink gums may turn red, indicating inflammation.
- Gum tissue covering teeth: In severe cases, the overgrowth can extend over part of the tooth surface, obstructing proper cleaning.
- Bleeding: Gums may bleed during routine activities such as brushing or flossing, which is a sign of gum irritation or damage.
- Persistent bad breath: Accumulated bacteria in the overgrown tissue often leads to unpleasant odors, even after cleaning the mouth.
- Discomfort or pain: Gum swelling can cause soreness, particularly during eating or speaking.
These symptoms can make routine oral hygiene challenging, leading to an increased risk of complications such as cavities or periodontal disease.
- Clinical examination: A thorough visual and physical inspection of the gums helps identify overgrowth and inflammation.
- Medical history review: The dentist evaluates any current or past health conditions and medications that may contribute to gum changes, such as anticonvulsants or immunosuppressants.
- X-rays and imaging: In some cases, X-rays are used to assess underlying bone and tissue health.
- Biopsy: If the diagnosis remains uncertain or if other conditions are suspected, a small sample of gum tissue may be taken for further testing to rule out diseases like oral cancer.
Timely diagnosis is crucial to prevent the progression of gingival hyperplasia and related complications.
Regular dental check-ups allow professionals to identify gum abnormalities early and recommend appropriate treatments.
Treatment Options
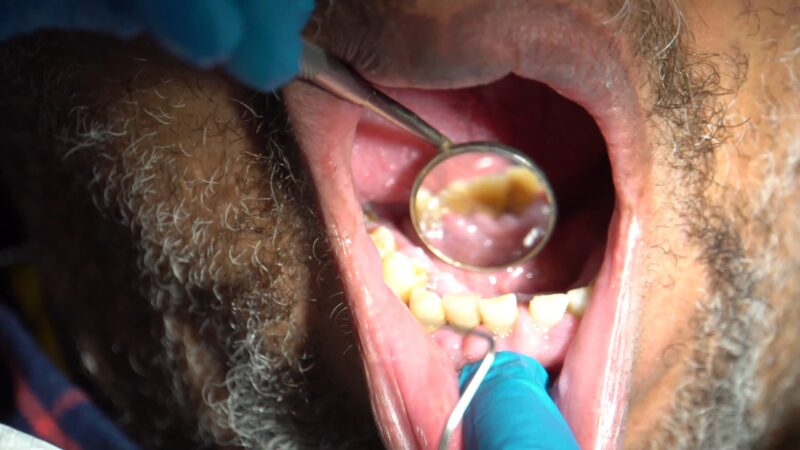
Treatment for gingival hyperplasia involves addressing the underlying causes and alleviating the symptoms to restore gum health. Of course, it is of the utmost importance to find a professional, like TannlegeTeam Dentist, who will take proper care of your case.
A combination of daily care, professional intervention, and in some cases, medical or surgical approaches is typically employed.
Improved Oral Hygiene
Daily brushing with a soft-bristled toothbrush helps remove plaque without irritating the gums further. Flossing between teeth removes food particles and plaque from areas a toothbrush cannot reach. This can also effectively prevent yellow teeth in the long run.
Using an antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce bacteria contributing to gum irritation and overgrowth. Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential in controlling plaque and tartar buildup, which are primary triggers for gum irritation and swelling.
Professional Dental Cleaning
Dentists use specialized tools to remove hardened tartar and plaque that regular brushing cannot address. Cleaning beneath the gum line prevents further irritation and supports healthier gums.
Scheduling regular cleanings ensures that gum overgrowth is kept in check and does not progress. Professional cleanings are vital for managing advanced cases where tartar has hardened and cannot be removed at home.
Medication Adjustment
For patients whose gum enlargement is caused by certain medications, healthcare providers may suggest alternative treatments. Adjusting dosages or switching to a different medication class can reduce gum overgrowth while still treating the primary condition.
Close communication between the dentist and physician ensures that both oral health and medical needs are balanced. Medication-related cases require careful consideration, as the overgrowth is often a side effect of necessary drugs such as anticonvulsants or calcium channel blockers.
Surgical Intervention
Gingivectomy is a procedure that involves the removal of excess gum tissue to reshape the gumline and restore normal function and aesthetics.
Laser Therapy is a modern, precise option that uses lasers to remove overgrown tissue with minimal bleeding and faster recovery.
Surgical methods are typically reserved for severe cases where non-invasive treatments do not provide relief. Laser therapy is particularly effective due to its accuracy and reduced discomfort during the procedure.
Prevention Strategies

Preventing gingival hyperplasia starts with proper oral hygiene. Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and flossing regularly helps keep plaque under control. Using an antibacterial mouthwash can further support gum health.
Regular dental check-ups are essential for early detection of any gum-related issues. Professional cleanings and examinations can identify potential problems before they worsen.
A healthy lifestyle also supports gum health. Avoiding tobacco and consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can enhance oral hygiene efforts. Foods high in vitamin C and calcium are particularly beneficial for maintaining strong gums.
When to Seek Professional Help
Seeking professional help becomes necessary when gum overgrowth persists despite good hygiene practices.
Swelling that causes discomfort or difficulty maintaining oral cleanliness warrants immediate attention.
Additionally, any concerns regarding the gums’ appearance should be evaluated by a dental professional.
Early intervention ensures timely management, preventing complications and preserving oral health.

